Example:
A researcher wants to find whether there is significant association between level of maternal education and birth weight of new borns. The study revealed following findings. Apply an appropriate statistical test whether maternal education and birth weight are independent?
| |
Illiterate |
Primary |
Secondary |
Graduate |
Post Graduate |
Total |
| Low birth weight babies |
10 |
12 |
15 |
9 |
10 |
56 |
| Normal birth weight babies |
20 |
25 |
35 |
45 |
55 |
180 |
| Total |
30 |
27 |
50 |
54 |
65 |
226 |
Solution:
Here, r = 2, c= 5. (Please do not count row or column for totals)
After putting these values, we get following output
Results
Chi Square = 8.153
Degrees of freedom = 4
p = 0.0861
The p value is not significant at alpha = 0.05.
Cramer's V = 0.1859
Phi (Φ) = 0.1859
Steps
1. Null hypothesis and Alternate Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis
There is no association between the variables. OR
The distribution of outcomes in groups is independent of groups.
Alternate Hypothesis
There is significant association between the variables. OR
The distribution of outcomes in groups is dependent on the groups.
2. Test Statistics
A. Based on given observed values in each cell, expected values for each cell are calculated using the formula
Ei = RTi * CTi / N. Where RTi and CTi are the row total and column total for observation i. N is the grand total.
B. Chi-squares value is calculated using the formuls
 Where Oi and Ei are observed and expected values for each cell.
Where Oi and Ei are observed and expected values for each cell.
C. Alternately Chi-square value can also be calculated directly, without need of expected value, using Mumbare's method.
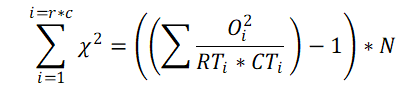
3. Degrees of freedom
Based on the number of groups (rows: r) and number of colums (c) degrees of freedom(df) is calculated as (r-1)*(c-1)
4. P value
Based on df and calculated chi-square value, p value is calculated using either chi-square table or a software.
5. Interpretation
If p < = alpha, reject the null hypothesi. Accept the alternate hypothsis.
If p > alpha, accept the null hypothesis (study failed to reject NH)
@ Sachin Mumbare